Treatment room of the future

In our previous radiation therapy blog – The Final Frontier of Radiation Therapy – we already described how the clinical and technological advances in the whole family of radiation therapy modalities have brought the world of radiation oncology to the threshold of a revolution in consolidation and optimisation.
Manufacturers of radiation therapy devices, especially particle therapy and BNCT devices, are under pressure to standardise their equipment, subsystems and software, lower costs of operation, and improve the extensibility of their systems to enable tomorrow’s solutions.
In this blog, we will discuss the technologies of the treatment room of the future and how its upgradable software, such as the OncologyOne suite, must consider all the technical requirements of the approaching paradigm shift.
Technologies converging in the modern treatment room
The advanced treatment room should be designed as part of an optimised particle therapy device architecture, tightly integrated with the beam source. With greater standardisation, the therapeutical value and cost-effectiveness of particle therapy (PT) and boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), can be increased significantly.
It is already clear that particle therapy will be enhanced by faster computation, better and streamlined workflows, and improved imaging to handle higher patient throughput, various modalities and specialised hardware. The latter will also enable game-changing paradigms for particle therapy, such as online adaptive technology and flash, to become economical with a significantly lower cost of ownership.
The future treatment room will strengthen efficacy and patient outcomes by incorporating technologies and solutions, such as:
- beam generation and delivery;
- new irradiation paradigms, e.g.:
- online Adaptive Radiation Therapy (ART);
- flash technology for PT;
- beam end-point optimisation;
- gantry optimisations (for PT);
- optimisations for fixed beamlines, e.g.:
- extended BNCT collimators;
- advanced therapy in-room imaging;
- image guidance;
- patient orientation and positioning;
- enhanced safety systems;
- innovative software architecture, e.g.:
- treatment management enhancements with software;
Beam generation and delivery
Regardless of the external-beam radiation therapy (RT) modality, it is of the utmost importance the device accurately and safely delivers the prescribed radiation dose to the patient by a well-controlled beam.
Particle therapy is the type of radiation therapy that is particularly useful in treating deep-seated tumours, for example, in the head or abdomen, while inflicting less collateral damage to the patient’s healthy tissue. A PT device consists of various subsystems, of which the closest to the patient is the scanning (dose delivery) system.
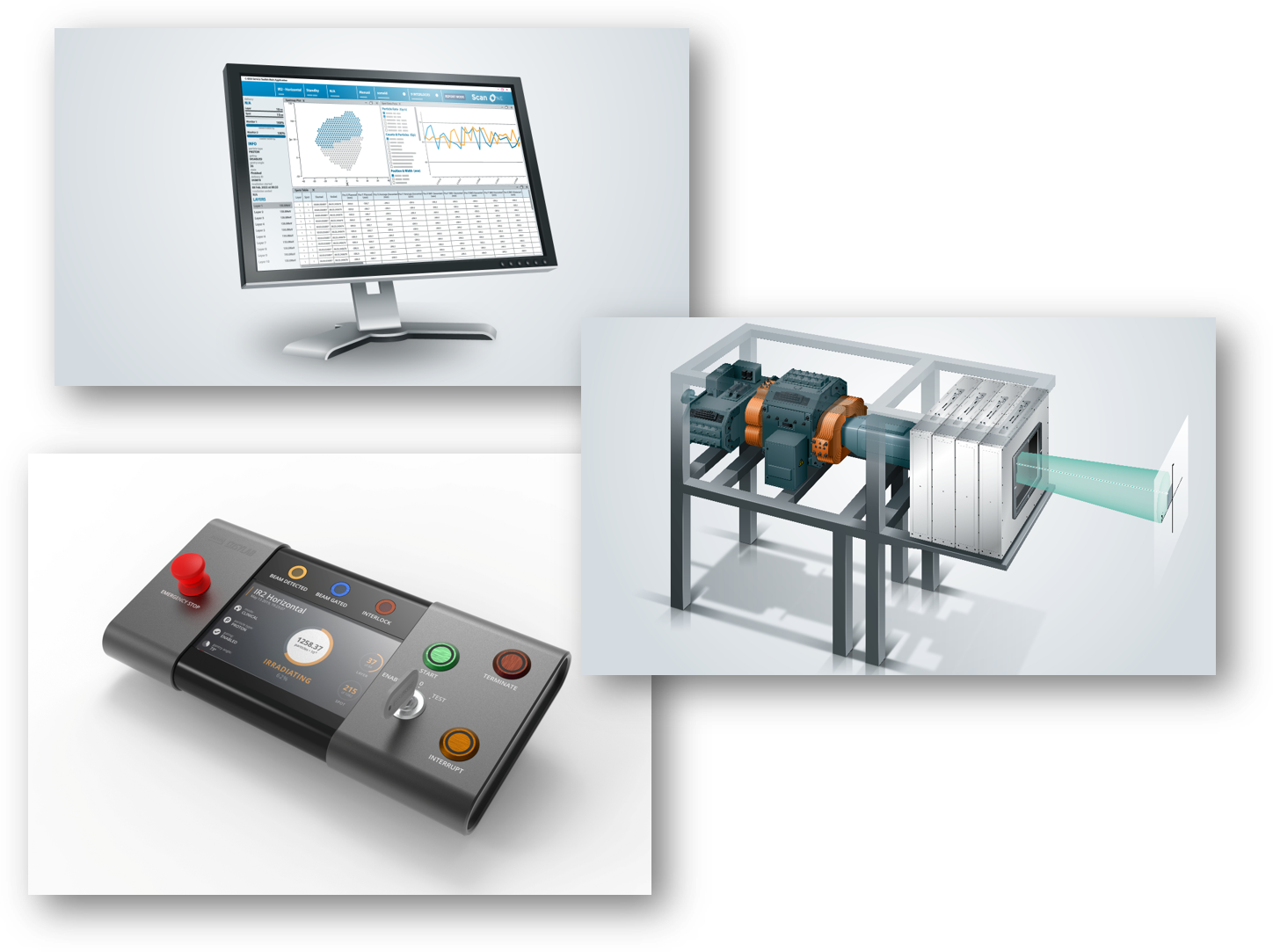
The PT device’s software must accurately control and monitor, in real-time, all clinically relevant parameters of the scanned particle beam. An effective dose delivery system such as ScanOne from the OncologyOne suite of medical software increases the number of patients being treated, shortens the average treatment time, and improves patient outcomes.
A modern particle therapy device should also support advanced types of beam delivery, such as pencil-beam scanning with protons. ScanOne does not have to turn the beam off between scanning spots and controls the particle rate control dynamically. The system automatically controls the beam intensity based on the weight of previous, current, and next spots.
Conventional, uniform scanning works by employing devices such as compensators and apertures that precisely adjust the dose to each patient’s treatment volume. Because of this, the duration and cost of treatments are longer, and delays are more significant than with pencil-beam scanning. The latter enables more treatment flexibility and delivers less secondary radiation to the patient, which is created by the patient-specific devices that adjust the dose.
New irradiation paradigms
Radiation oncology has been experiencing a renaissance in the last decade. One of the hot research areas is online adaptive radiation therapy (ART) which is being funded, among others, by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 programme. The international RAPTOR project, which Cosylab co-founded and of which it is a prominent member, brings Real-time Adaptive Particle Therapy of cancer to the clinic.
ART is a treatment paradigm that more accurately targets cancer by reckoning with ongoing changes in the patient’s anatomy (internal organ movement, body-fat and tumour-size changes) and physiology. During a course of radiation therapy, ART modifies the radiation treatment plan following the changes in the patient.
Adaptive radiation therapy relies on several components, namely in-room image guidance, deformable image registration, automatic recontouring, plan evaluation and re-optimisation, dose calculation, and quality assurance. As ART is closely dependent on precise patient positioning, the PositionOne product supports the adaptive radiation therapy features in total to bring more accurate and efficient treatment delivery. Designed for the future, the imaging-support system PositionOne enables adaptive radiation therapy and dose-driven patient treatment out of the box.

Flash technology and hypofractionation
Another cutting-edge advancement is FLASH proton therapy. It offers an innovative way to dramatically decrease the number of fractions to complete a patient’s treatment, lower the time for dose delivery to mere seconds, and spare healthy tissue.
For FLASH to be clinically applicable, device hardware and software must generate significantly higher beam currents, faster energy adjustments and hundreds of times quicker full pencil-beam scanning than with conventional systems.
Modern software, like ScanOne, must be fully compatible with the functionalities of the future treatment room, such as FLASH, adaptive proton therapy, real-time tracking, proton imaging, range verification, and arc therapy. The software’s architecture should be modular, allowing for easy integration into a multitude of existing PT systems and customisation with vendor-specific features, regardless of accelerator type or particle species used.
Image guidance radiation therapy
Radiation therapy with image guidance (IGRT) is a method that closely couples imaging techniques with irradiation during each treatment session to improve the precision and accuracy of treatment delivery.
IGRT will be used increasingly to adjust the radiation treatment of patients whose tumour and organ locations deviate from initial imaging setups. Future systems will be capable of supervising organ motion, tumour changes and weight variations from day to day.
To illustrate, OncologyOne’s module PositionOne guarantees effective image guidance with patient positioning verification and is ready to integrate existing and new imaging and verification modalities. Software for the coming times combines image-guided RT with intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to match the radiation dose as closely as possible to the distribution and depth of cancer cells.
Furthermore, using in-room proton-beam imaging we will achieve more efficient and safer online alignment and verification of a patient in the treatment position. The overall cost of therapy planning in PT will be lower with proton imaging, allowing for more precise treatment. And artificial intelligence (AI) will streamline the whole treatment workflow, enabling clinical teams to be more effective and less overwhelmed.
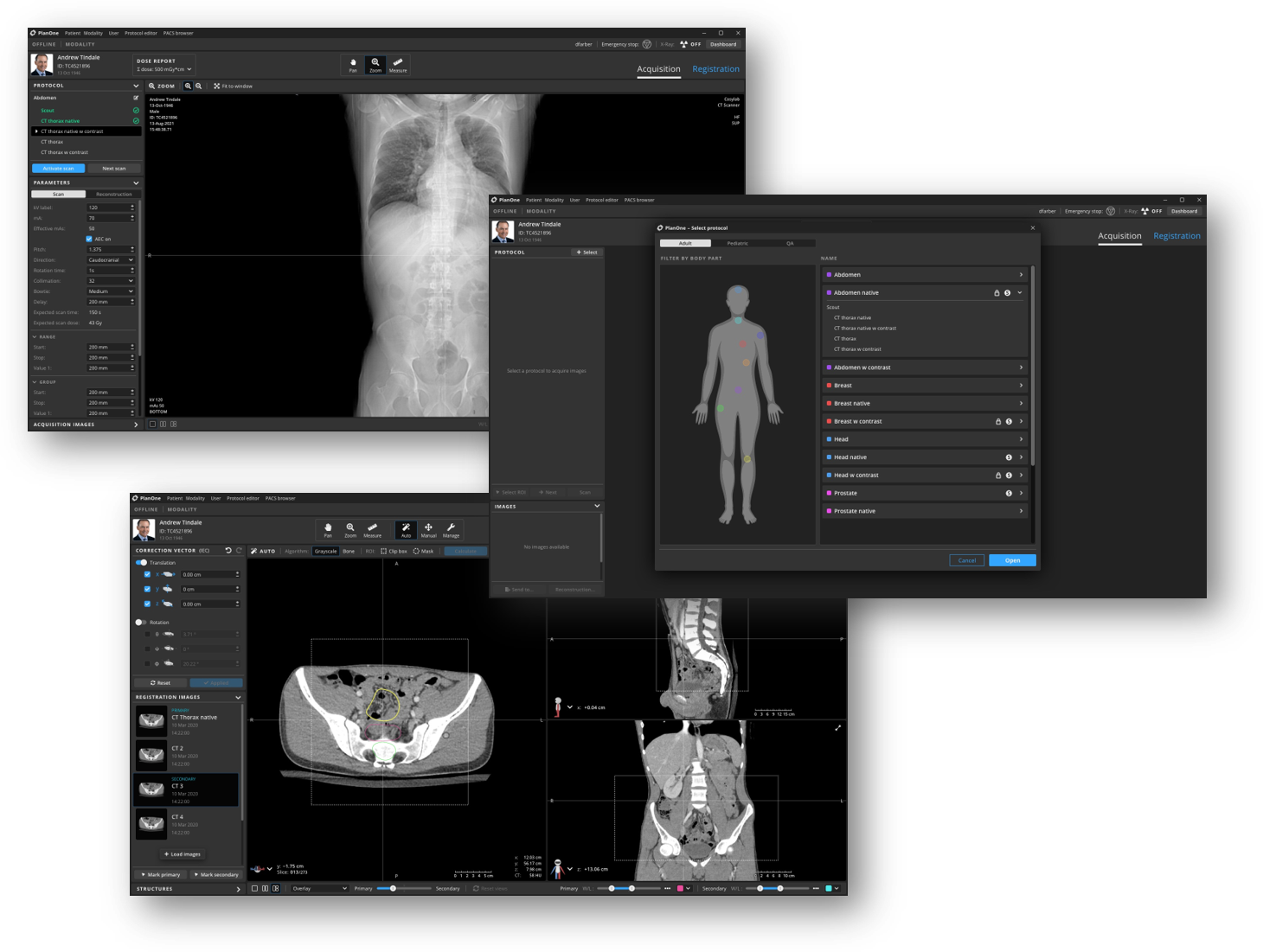
Advanced therapy in-room imaging
Advanced therapy in-room imaging is closely connected to image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) – it is, in essence, the basis of the latter’s imaging functionality.
The treatment room of tomorrow and its medical system software should support all imaging devices and functionalities, such as:
- CBCT (gantry- and PPS-mounted, on-rails);
- X-ray (gantry- and floor-mounted);
- in-room CT (PPS-mounted, on-rails);
- proton imaging.
Each type of imaging brings its specific improvement to the overall treatment system. For example, proton imaging boosts the effectiveness of proton therapy by increasing the accuracy of the relative stopping power (RSP) calculation.
The resulting proton treatment plans can be more accurate, allowing for much narrower beam fields while providing more conformable treatment. Furthermore, measured doses for proton imaging are 10 to 100 times lower than for CT imaging. This could enable frequent proton imaging before each treatment fraction, with negligible adverse effects on the patient.
The PositionOne software supports current and future imaging modalities and devices used in a variety of treatment room configurations. The module utilises advanced algorithms to perform the required imaging in real-time and for specialised modes. In-room imaging software should integrate seamlessly with the treatment workflow, allowing for simple upgrades and support of new imaging modalities.
Patient orientation and positioning
More and more clinicians are now rethinking how to best set the patient up for particle treatment. Is it best for the patient to be resting and prone, or does one put them in a seated, perched position or fully upright? Of course, it depends on the type of the beam and the specific cancer and tumour location. For treatment rooms with a gantry and variable beam direction, a lying down position for the patient on the treatment couch is the best.
However, when a clinic needs a lower total cost of ownership and shorter installations times, fixed-beam treatment and the patient’s “upright and rotating” positioning has several advantages. For example, upright positioning facilitates faster imaging and patient setup in treatment rooms without a gantry.
The next revolution awaiting the treatment room – already supported by The PositionOne module of OncologyOne – is augmented patient positioning systems with “smarter” and faster verification and increased use of robotic positioners and transporters, especially for boron neutron capture therapy.
Treatment management enhancements with innovative software
Tomorrow’s treatment room will demand software innovation to manage the whole treatment process, including planning, dose delivery and clinical workflow.
A few years ago, offline adaptive radiation therapy consisted of treatment planning and quality assurance. If you found your patient was deviating after you started a course of treatment, you had to perform replanning, which is a time-consuming task. Even today, oncologists rarely perform online adaptive radiation therapy, as most treatments are associated with high-toxicity risks. These issues will be relieved by new software solutions for treatment planning, such as automatic delineation, that are based on artificial intelligence.
Deep learning solutions can speed up and standardise the contouring of organs, based on CT or MRI, to automatically annotate, for example, more than 150 structures in the brain in a few dozens of seconds. Advanced software can generate a fully planning-compatible synthetic CT within seconds from MRI images. Soon, AI-based treatment planning solutions will automatically determine the specific constraints that can be used for a patient given the tumour’s location and the physician’s prescription.
Future-proofed software solutions such as TreatmentOne, PositionOne and WorkflowOne are tightly intermeshed with therapy device functionality and will be fully capable to exploit the device’s potential and increase patient throughput. TreatmentOne is an easily configurable treatment control system for radiation therapy, ready to be integrated into any oncology workflow. On the other hand, WorkflowOne is a management product for adaptive therapy workflows, tightly interoperable with other hospital informational systems.
Artificial intelligence will, eventually, streamline the whole treatment workflow and minimise user interaction, especially in online adaptive radiation therapy, which will become a regular feature in the treatment room of the future.

The treatment room on the horizon
Hospitals are increasingly under stress to provide successful and timely cancer treatment to a growing number of patients and do so in a cost-controlled manner. At the same time, manufacturers of particle therapy and BNCT devices are more than ever obliged to design upgradeable and long-lived, future-proof designs. The latter must take into account the long-term economics of operating a complex device – and the increase in patient throughput and cancer treatment efficacy.
The name of the game is lowering the total cost of ownership for particle therapy which promises less toxicity, shorter recuperation times and better outcomes than conventional RT– with a clear financial and health advantage for the health care systems clinics and patients.
All the advances come together in the treatment room, marking it the final frontier of particle therapy. Well-tested medical software that has been designed from the ground up to support all future particle therapy paradigms will help hospitals and manufacturers to reach this frontier with success.
